Back in early February 2023, Google’s Bard AI gave an incorrect answer about the James Webb Space Telescope during a public demonstration ahead of Bard’s official release. It effectively confused it with another space telescope. As a result of what seemed like a minor mistake, Google’s parent company saw its stock price drop by around 9%. Still, over the past few years, AI for web development has evolved from an interesting experiment into a fully fledged working tool. Today, it is part of everyday practice: generating design mockups, writing code, optimizing page load speed, and creating content. For businesses, this set of capabilities sounds appealing – who wouldn’t want to launch a website faster, cheaper, and without relying on a large team?
But alongside these opportunities comes an important question: where is the line between smart automation and risky delegation of responsibility to an algorithm? Fully automated projects do offer a fast start, but they often break down at the scaling, SEO, or conversion stages. At the same time, purely manual development remains reliable, yet for many companies it is too slow and too expensive. An increasing number of industry studies point to the same conclusion: a hybrid approach (AI + human) enables faster business results. According to IBM, hybrid IT projects that combine automation with human expertise deliver more than a threefold ROI over five years, while the time to achieve a positive ROI is reduced by roughly 40–50% compared to extreme models – either fully automated or entirely manual development.
So today, the real question is how to properly distribute roles between technology and humans.
In this article, we will look at:
- which tasks AI already performs effectively today;
- where automation starts to harm the business;
- what should remain in human hands in 2026;
- what an optimal hybrid model of website development looks like in practice.
What AI Already Does Better and Faster Than Humans
Today, a website can be built in a single evening without a designer, a developer, or even a clearly defined technical specification. AI website creation sounds like an ideal scenario for many businesses. However, it’s important to understand one thing: AI does not work brilliantly everywhere; it works best on specific types of tasks. Wherever a process can be clearly described, repeated, and scaled, artificial intelligence delivers a real advantage in speed, cost, and initial flexibility.
So let’s break down where AI is truly strong today.
Design Mockups and Basic Interface Structure Generation
Imagine you have a product idea, but no clear vision for the website yet. In the past, this meant weeks of work with a designer, mood boards, concepts, and revisions. Today, AI can assemble the first visual skeleton of a website in just a few minutes. All it needs is a short description: who you are, who you work for, and what problem the site solves. As a result, you get:
- a homepage structure;
- basic typography;
- a color palette;
- block placement logic from hero to CTA.
To make this less abstract, it’s enough to look at how modern AI assistants work in web development. For example, in Copilot, the process doesn’t start with mockups or a technical brief, but with a simple text description of the future website. The AI then generates an initial version of the site structure.
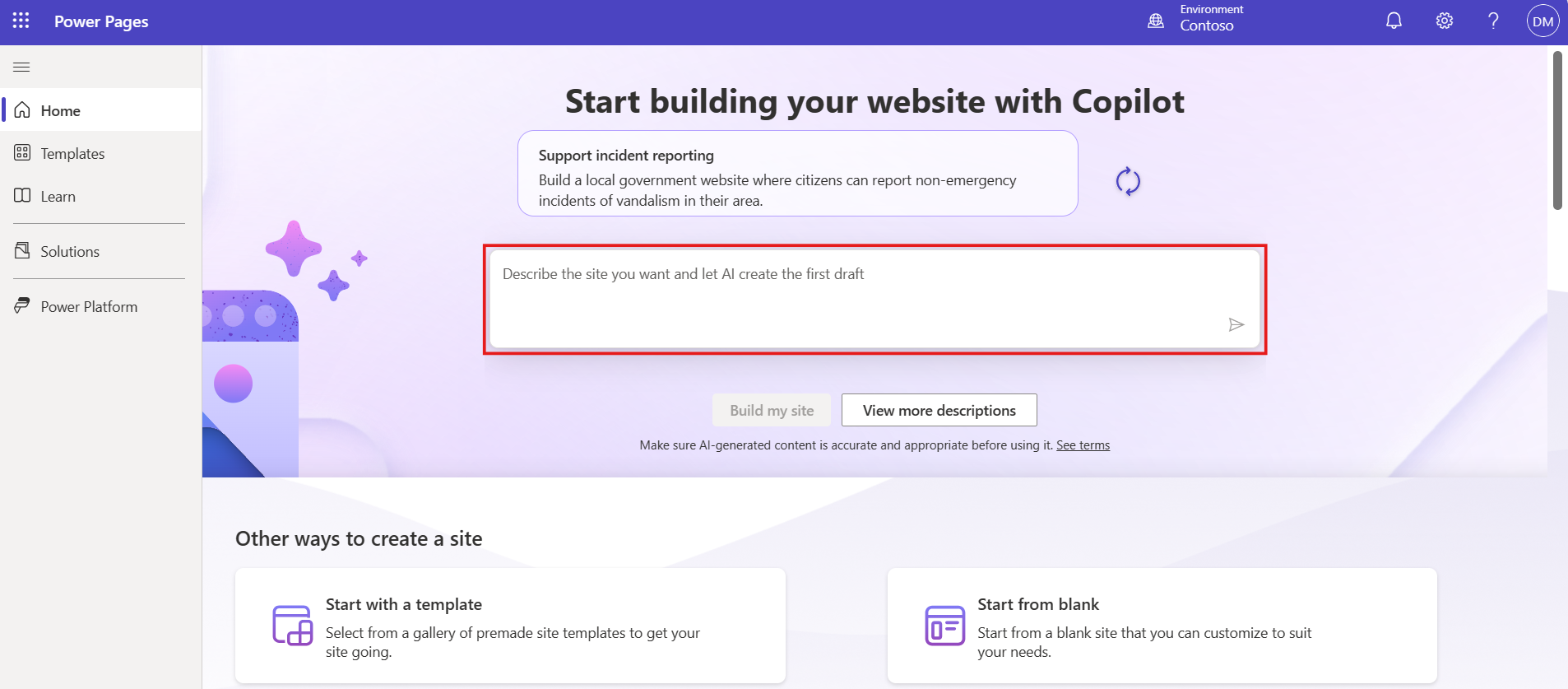
Example of an AI-powered website creation interface: the user describes the project idea, and the system automatically generates the first draft of the site structure.
This becomes a concrete reference point for discussion and decision-making, not just an abstract idea. Ask yourself: what’s easier – explaining a concept from scratch or reviewing a ready-made layout and refining it? This is exactly the stage where AI saves the most time.
Example: A startup is preparing an MVP for an online consultation service. An AI-powered web development tool generates 2-3 landing page variants with different angles: one focused on expertise, another on speed, and a third on value. The team immediately sees which direction resonates and moves forward without long initial iterations.
Automated Coding and Technical Optimization
Does a human really need to manually write every form, button, or standard page block? In most cases, no. Web development with AI project performs very well at generating boilerplate code and standard components. Algorithms quickly create reusable interface elements, basic page layouts, automated tests for common scenarios, and an initial technical structure for the site. A separate advantage is technical SEO. AI can easily generate meta tags, check heading hierarchy, analyze page load speed, and point out where the site slows down.
First-Level Content
A common question is: “Can AI write website content?” The answer is yes – with an important caveat. It excels at drafts: service descriptions, “About Us” pages, FAQs, and informational blocks. This is especially noticeable when the website is large and needs to be populated quickly. AI helps fill empty pages, establish content logic, and prepare a foundation for further editing.
An important note: this is not final content, but a starting version. However, it’s precisely this starting point that allows a website to go live without delays and for content to be refined later on a live project.
Chatbots and Personalization
Up to 70-80% of typical user inquiries can be handled automatically. This is where AI-powered chatbots come into play. They:
- answer standard questions;
- help users navigate the website;
- guide users toward a purchase or a lead submission.
In e-commerce and service-based products, AI also personalizes content: it shows relevant products, suggests the next step, and adapts offers based on user behavior. All of this has a direct impact on conversion rates.
You might also be interested in: How to use GPT for online business?
Where AI Starts to Do Harm When Too Much Is Delegated to It
Despite all its obvious advantages, AI website development has clear limits. When strategic decisions are delegated to artificial intelligence, it introduces risks that directly affect business outcomes. Why does this happen? Because AI optimizes what can be formalized. Business, branding, and human behavior, however, can only be partially formalized.
Template Thinking and Loss of Differentiation
You’ve probably seen websites that look fine at first glance but are completely forgettable. This is one of the most common side effects of excessive automation. AI is trained on vast volumes of existing solutions, so its outputs are often averaged. It reproduces what has worked in a templated way before, but it doesn’t create new meaning. As a result, a site can be clean, modern, fast, and technically correct – yet have no real character. For businesses in competitive niches, this is critical. When users see dozens of similar websites, they make decisions based on trust, emotion, and clear positioning. AI doesn’t know how you should differentiate yourself from competitors; it simply repeats patterns.
Pro Tip: Ask yourself: if you replaced the site's logo, would a user notice the difference? If not, that’s a clear warning sign.
SEO Limitations and Content Hallucinations
The most dangerous part of AI hallucinations is not the mistake itself, but how convincing it sounds. These errors are often delivered with confidence and authority, which makes users trust them without verification. This is not a marginal issue. According to a Deloitte survey, 77% of businesses using AI are concerned about hallucination risks. At the same time, the generative AI market reached $67 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at 24.4% annually through 2030. This means hallucination-related errors will increasingly affect real users making real business decisions based on false information.

Generative AI market size worldwide
The wording is logical and the terminology is correct, yet it repeats generic phrases, adds no real value, and often fails to address the actual user intent. So-called hallucinations are another AI weakness: facts, examples, or claims are added that appear plausible at first glance but are inaccurate or entirely fabricated. Without editorial oversight, this type of content loses credibility – both with users and with search engines. In the short term, such a site may attract traffic. In the long run, however, it loses in SEO because it fails to meet EEAT requirements.
Lack of Business Context
AI lacks understanding of how decisions are made within your company. Without awareness of business goals, internal processes, legal constraints, and sales logic, algorithms end up optimizing form rather than substance. This becomes especially visible in complex B2B, service-based, or enterprise models. For example, AI-driven web development may propose a simple lead form flow that looks logical on the surface but completely ignores the real customer journey: approvals, decision-making stages, and the involvement of multiple stakeholders.
A Typical Case: When Everything Looks Good but Doesn’t Sell
The most common scenario looks like this: a website fully generated by AI looks great – it loads fast, has a modern design, a clean structure, and decent copy. Analytics show healthy traffic, but conversion rates are low. Why? The site fails to explain the product’s value to this specific audience. It uses the right words but doesn’t answer the user’s core question: why do I need this right now, and why should I choose you? In other words, the problem is that AI was delegated decisions that should have been made by a human.
What Is Critical to Leave to Humans
Key decisions that directly affect the business still require human thinking, accountability, and experience. There are several areas where delegating work to AI without human oversight creates more risk than value.
- Website strategy and business logic
Only a human can correctly answer the fundamental question: why is this website being created in the first place? Is it a sales tool, a lead generation channel, or a customer support interface? Or is it part of a long-term brand strategy? This decision defines the entire site logic – page structure, interaction flows, content priorities, and conversion points. If you rely solely on AI, algorithms will suggest a generic setup, but they cannot account for real business goals, internal KPIs, or the team's expectations. - Architecture and integrations
Complex projects almost always go beyond a simple website. Integrations with CRM, ERP, payment systems, analytics platforms, and internal services require systems thinking and a deep understanding of how the business operates internally. Mistakes at this level are often invisible at first, but over time they lead to failures, manual workarounds, and technical debt. This is where a human is essential – someone who understands the long-term impact of architectural decisions and takes responsibility for them. - UX/UI for emotional engagement
Why do some websites feel trustworthy while others do not? The answer often lies in subtle details: language, rhythm, and the logic of information delivery. UX research increasingly relies on actual user engagement time. For example, user behavior analysis published on arXiv shows that average dwell time is around 47 seconds on desktop and 72 seconds on mobile devices, with significantly higher figures for so-called inside users – an audience with a higher level of interest and engagement. Longer dwell time correlates with the quality of explanations, information flow, and contextual depth, all of which are shaped by human work on content and structure. - Quality control and security
Human-in-the-loop is no longer optional – it is a necessity. Human review at critical stages helps identify errors, logical gaps, security issues, and incorrect integrations. While website development AI is effective in supporting audits, the final decision must remain with a specialist. When it comes to data, access control, and system stability, the cost of a mistake is simply too high to delegate entirely to an algorithm.
Comparison of Approaches: AI, Human, and Hybrid (AI + Human)
When a business chooses how to build a website, the decision rarely comes down to budget or timelines alone. In reality, it is a choice between different models of responsibility, risk, and long-term impact. To understand the difference at the outcome level, it’s worth looking at these approaches systematically.
Comparison of approaches
| Criteria | AI Website Generators | Human-Driven Development | Hybrid Approach (AI + Human) |
| Speed of Launch | From a few minutes to 1-4 weeks. Extremely fast start, but often without deep refinement | On average, 2-8 weeks, depending on complexity and processes | Fastest for commercial projects: AI accelerates preparation, humans control critical decisions |
| Cost | Low initial cost or tool subscription | High upfront investment due to manual work | Medium: costs are optimized through automation of routine stages |
| Customization | Limited by templates and generator settings | Virtually unlimited | High: template-based foundation plus manual business-specific adaptation |
| UX and Branding | Standardized, designed for an average user | Highly dependent on team expertise | Balanced: AI builds the base, humans add emotional and semantic depth |
| SEO Potential | Basic: technical optimization without a deep strategy | Full: from structure to content | Strategic: automation combined with human SEO thinking |
| Risks | Template-driven output, content hallucinations, weak differentiation | Human factor, slower delivery, higher cost of mistakes | Minimized through a human-in-the-loop approach |
| ROI (Return on Investment) | Often short-term and limited | Stable but slow | Up to 50% faster ROI compared to extreme models |
The Future of the Web Developer’s Role in 2026+
In IT podcasts, you can often hear claims that AI tools like ChatGPT will eventually take jobs away from junior developers. In practice, however, we see something different: it’s not people's needs that are changing, but the nature of their work. Developers are becoming less like executors of isolated technical tasks and more like specialists who design systems, make decisions, and take responsibility for outcomes as a whole.
A major shift is the ability to work with uncertainty. AI in website development performs well when dealing with clearly defined, formalized tasks, but it struggles with non-standard situations, trade-offs, and business constraints. This is where the human role becomes essential. In 2026, the most valued professionals are not those who can write code, but those who understand how technical decisions affect the product, processes, and users.
Conclusion
In summary, no AI service is a magic wand that can instantly create a perfectly optimized website with thoughtful design and flawless content. Today, AI-based tools play a more apprentice role: they take on routine, repetitive tasks and help teams save time. However, final responsibility always remains with humans – someone must verify that the content contains no inaccuracies and that AI hasn’t invented its own programming language for a simple button.
The most effective web development happens where roles are clearly defined. An AI website builder handles routine tasks, speeds up preparation, and assists with prototyping and technical optimization. Humans, compared to an AI website builder open source, are responsible for meaning: strategy, architecture, interaction logic, user trust, and accountability for the final result. This balance enables websites to launch quickly and function as full-fledged business tools.
Read more articles in our blog
-compress.jpg)



